Open-source workflow engine
Orchestrate and observe computational workflows defined in plain Python. Suitable for data pipelines, background tasks, agentic systems.
import coflux as cf
import requests
@cf.task(retries=2)
def fetch_splines(url):
return requests.get(url).json()
@cf.task(cache=True)
def reticulate(splines):
return list(reversed(splines))
@cf.workflow()
def my_workflow(url):
reticulate(fetch_splines(url))Monitor
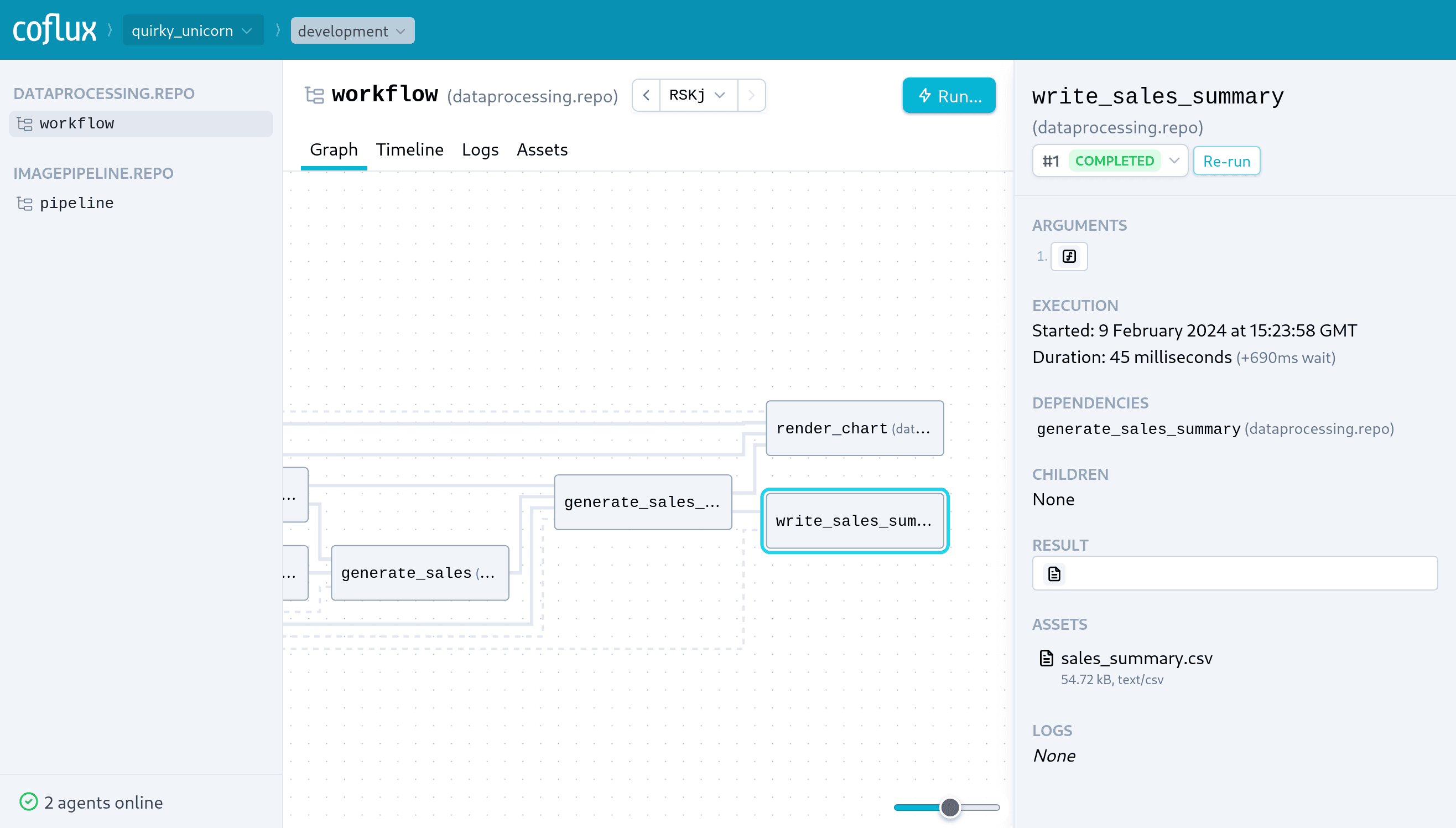
Real-time observability
Watch workflows execute in real-time in the graph-based web UI. Debug issues within a workflow by re-running problematic steps.
Build
Developer friendly
$ pip install coflux$ coflux server
Server started. Running on port 7777.$ coflux worker --dev my_example.repo
Connecting (localhost:7777, pSTtDMx, production)...
Connected.Deploy
Worker-based architecture
Maintain control of deploying workers in your own infrastructure. Coflux takes care of orchestrating execution of tasks onto the available workers.
Debug
Turbo-charged triage
- Inspect arguments, results and errors in the web UI.
- Re-run failing production tasks in a separate 'spaces', executing in your development environment.
- Memo-ise side-effecting (or slow) tasks so that you can re-run a workflow without re-running the task.
@cf.task(memo=True)
def send_notification(...):
mailer.send(...)Use cases
Data pipelines
Background tasks
Control systems
Bioinformatics
Model training
AI agents
Features
Batteries included
Easily enable per-step features as needed and focus on business logic. Sensible defaults that can be customised as needed.
Distributed execution
Start up as many workers as needed, and Coflux will distribute the workload between them.
Low-latency
Scheduled tasks are run in isolated processes, and start in milliseconds.
Caching
Enable caching for a task to have the result be re-used across runs.
Debouncing
Defer execution of a task - e.g., to send a user notification - until tasks have stopped being scheduled.
Retries
Automatically retry failed tasks (with exponential backoff). Or manually trigger retries of individual steps from the UI.
Logging
Follow log messages in real-time. Include variables and references to executions and assets.
Assets
Share files and directories between steps. Inspect and preview contents in the UI.
Sensors
Build sensors to react to events in your system in real-time, and reliably trigger workflow runs.
Join the mailing list
Get notified of new product features.